Acute Aortic Symptoms
What Are Acute Aortic Syndromes?
Acute aortic syndromes are some of the most dangerous cardiovascular emergencies that can happen to a person. They occur when the wall of the aorta, the body’s largest artery, suddenly becomes damaged. Because the aorta carries blood from the heart to the entire body, any tear, bleeding, or weakness in it can rapidly become life-threatening.
Even though they are rare compared to other heart and vascular diseases, acute aortic syndromes are extremely important because they can cause sudden death if not recognized and treated immediately. For this reason, they are often described as the most dangerous condition of the cardiovascular system. Fast diagnosis and urgent medical attention are critical.
Different Types
Doctors group three main conditions under the term “acute aortic syndromes”:
Aortic dissection: The most common form. A tear develops in the inner layer of the aorta, allowing blood to force its way between the layers of the vessel wall. This can create a false passage for blood, blocking vital blood flow and risking rupture.
Intramural hematoma: Bleeding within the wall of the aorta, often caused by small vessel ruptures inside the wall itself. It can behave very much like a dissection and present with many similar symptoms if untreated.
Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer (PAU): Structural damage caused by long-term hardening of the arteries. An ulcer “burrows” into the wall of the aorta and may lead to bleeding, dissection, or rupture.
Although these types look different, their risks are similar, which is why they are grouped together as one syndrome.
Warning Signs
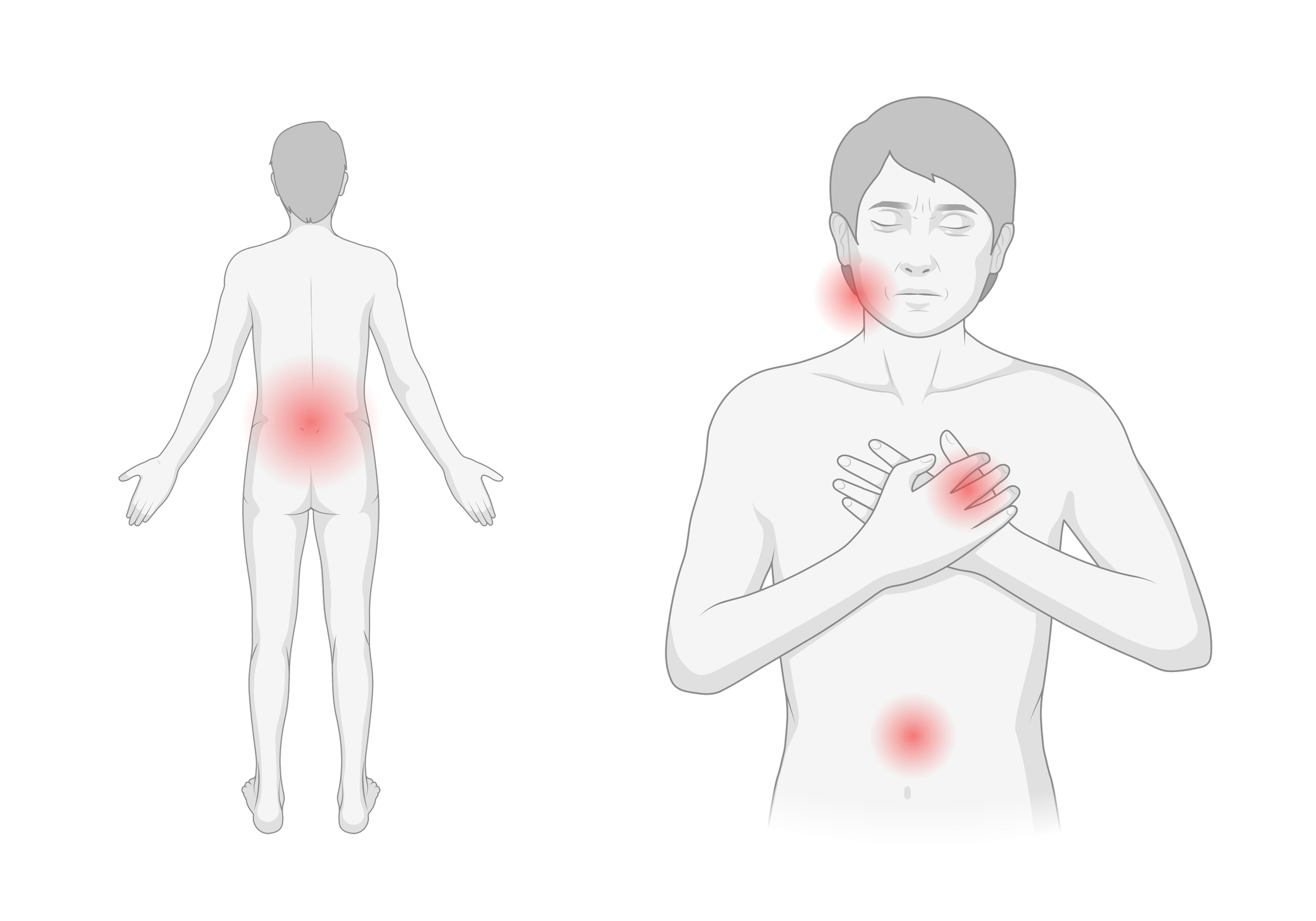
The hallmark of acute aortic syndromes is sudden, intense pain. Patients often describe it as sharp, tearing, or ripping. The pain may occur in:
The chest
The back
The abdomen
The neck or jaw
Other possible warning signs include:
Pain that shifts location as the condition evolves
Sudden shortness of breath or sweating
Dizziness, fainting, or weakness
Weakness, numbness, or unequal pulses in arms and legs
Because these symptoms can mimic other conditions, especially a heart attack or stroke, it is critical not to ignore them. Immediate emergency medical help is essential.
Complications
If acute aortic syndromes are not treated promptly, they can lead to severe complications, such as:
Aortic rupture: A complete break in the wall of the aorta, often fatal within minutes
Organ damage: If blood flow to kidneys, brain, or other organs is blocked
Stroke-like symptoms: If vessels leading to the brain are affected
Heart problems: Such as damage to the heart valves, heart failure, or bleeding around the heart when the dissection is close to the heart
These risks explain why time is critical: the longer treatment is delayed, the higher the chance of life-threatening complications.
How Are They Treated?
Treatment depends on the exact type of acute aortic syndrome and where in the aorta it occurs. General strategies include:
Emergency surgery: Often needed for severe dissections near the heart (ascending aorta). The damaged part is replaced or reinforced with a graft/prosthesis. Examples include aortic replacement, as well as combined hybrid approaches such as the frozen elephant trunk.
Endovascular stent grafts: A minimally invasive approach where a stent (a fabric-covered metal tube) is placed inside the aorta to seal the tear or ulcer from the inside. Examples include any form of so called endovascular aortic repair, especially in the chest cavity (TEVAR).
Medication: Drugs to quickly lower blood pressure and heart rate, reducing strain on the aortic wall. These are also used for long-term treatment after surgery.
Close monitoring: In certain cases, especially smaller dissections or intramural hematomas, treatment focuses on careful observation through repeated imaging scans and medical therapy.
Each treatment approach carries its own benefits and risks, and the decision depends on the patient’s condition, the part of the aorta involved, and overall health.